2024-04-08T06:32:17
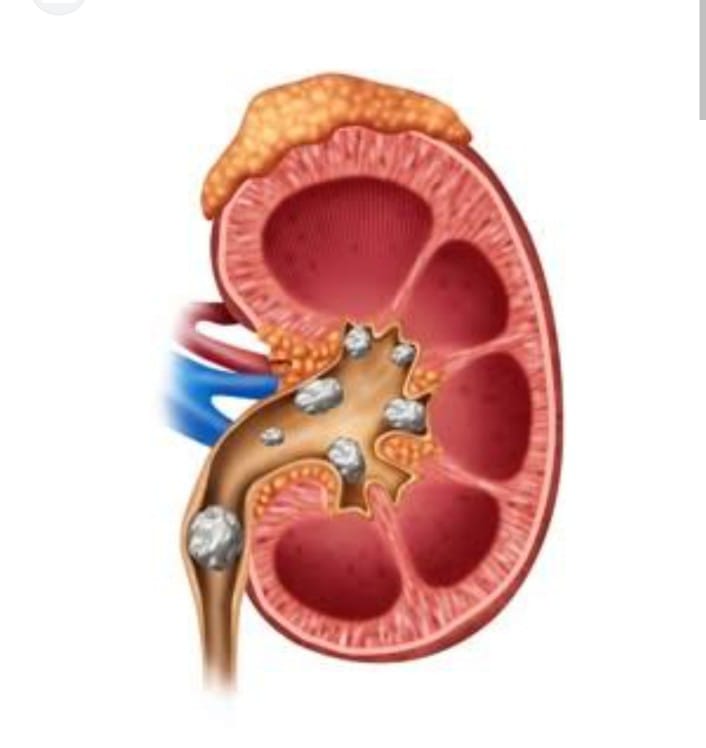
Integrity Hospital nephrology department is dedicated to kidney care What are Kidney Stones? Kidney stones are solid masses made up of crystals that can form in the kidneys when there is a buildup of certain substances, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid. These stones vary in size, ranging from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. Causes of Kidney Stones: Dehydration: Lack of sufficient water intake can lead to concentrated urine, making it easier for kidney stones to form. Dietary Factors: Consuming foods high in oxalate, sodium, or animal proteins can increase the risk of kidney stone formation. Family History: A family history of kidney stones can predispose an individual to develop them. Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions such as hyperparathyroidism, urinary tract infections, and inflammatory bowel disease can increase the risk of kidney stones. Medications: Certain medications, including diuretics and antacids containing calcium, can contribute to kidney stone formation. Symptoms of Kidney Stones: Severe pain in the back, side, or lower abdomen Painful urination Blood in the urine Frequent urge to urinate Cloudy or foul-smelling urine Nausea and vomiting Fever and chills (if there is an infection) Diagnosis of Kidney Stones: Diagnostic tests for kidney stones may include: Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds can visualize the presence and location of kidney stones. Urinalysis: A urine sample can be analyzed for blood, crystals, and other substances that may indicate kidney stones. Blood Tests: Blood tests can evaluate kidney function and identify any underlying metabolic disorders that may contribute to stone formation. Treatment Options: Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or prescription medications can help alleviate pain associated with kidney stones. Hydration: Drinking plenty of water is essential to help flush out kidney stones and prevent new ones from forming. Medications: Medications may be prescribed to help dissolve certain types of kidney stones or to control underlying conditions contributing to stone formation. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): This non-invasive procedure uses shock waves to break up kidney stones into smaller pieces that can be passed more easily. Surgical Removal: In cases where kidney stones are too large to pass on their own or are causing complications, surgical procedures such as ureteroscopy or percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) may be necessary. Prevention Tips: Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Follow a balanced diet low in sodium and high in calcium. Limit consumption of foods high in oxalate, such as spinach, rhubarb, and nuts. Maintain a healthy weight and engage in regular physical activity. Consult with a healthcare provider to monitor and manage any underlying medical conditions or medications that may contribute to kidney stone formation. Conclusion: Kidney stones can be a painful and recurrent condition, but with proper diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures, they can be managed effectively. If you suspect you have kidney stones or are experiencing symptoms, it's crucial to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications and receive appropriate care. keywords: people also ask for : most searches on : #besthospitalinnagpur #besthospitalnearme #kidneyhospitalnearme #tophospitalinumredroad #kidneyhospitalindighori #tophospitalinsakkardara #kineyhospitalindighori #kidneystoneoperationhospital #kidneyhospitalinumredroad #kidneyhospitalindighori