2024-04-02T09:33:44
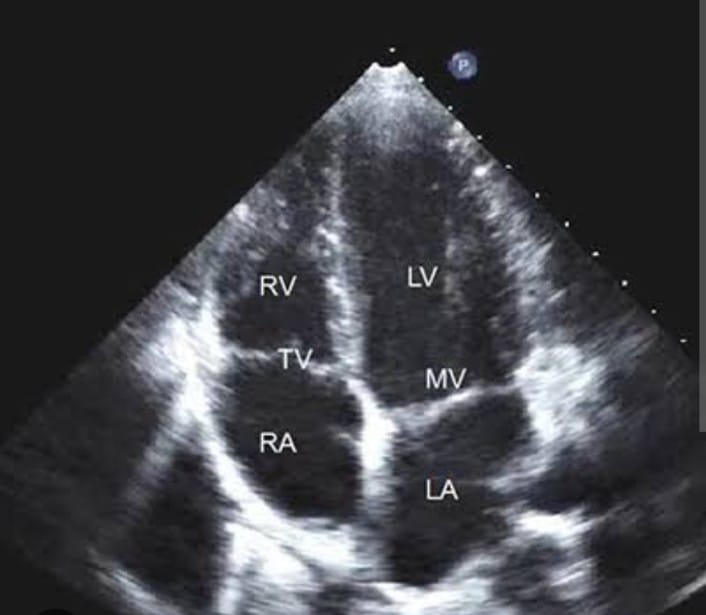
Echocardiography is a non-invasive diagnostic imaging technique that uses ultrasound waves to create detailed images of the heart's structure, function, and blood flow. It plays a crucial role in the evaluation, diagnosis, and management of various cardiovascular conditions, providing valuable insights into cardiac anatomy, chamber dimensions, wall motion abnormalities, valve function, and hemodynamics. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the principles, types, indications, procedure, and clinical applications of echocardiography. Principles of Echocardiography Echocardiography operates on the principle of ultrasound technology, utilizing high-frequency sound waves (typically between 2 to 18 MHz) that are transmitted and received by a transducer placed on the chest wall. These sound waves penetrate the body tissues and are reflected back when they encounter boundaries between different tissues or structures in the heart. The reflected waves are then converted into electrical signals, which are processed by a computer to create real-time images of the heart. Types of Echocardiography Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE): Procedure: A transducer is placed on the chest wall to obtain images of the heart through the chest wall. Indications: Evaluation of cardiac structure, function, and wall motion; assessment of valve abnormalities; detection of congenital heart defects; screening for cardiomyopathies and pericardial diseases. Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE): Procedure: A specialized probe with an ultrasound transducer is inserted into the esophagus to obtain closer and clearer images of the heart structures. Indications: Detailed assessment of cardiac valves, atrial appendages, and prosthetic devices; evaluation of intracardiac masses, thrombi, and aortic diseases; guidance for interventional procedures. Stress Echocardiography: Procedure: Echocardiography is performed before and after exercise (treadmill or pharmacological stress) to evaluate cardiac function and blood flow under stress conditions. Indications: Detection of coronary artery disease, assessment of myocardial viability, evaluation of valvular and myocardial diseases, risk stratification for cardiac events. Doppler Echocardiography: Procedure: Utilizes Doppler ultrasound to measure and visualize blood flow velocities and direction within the heart and great vessels. Indications: Assessment of valvular stenosis and regurgitation, detection of intracardiac shunts, evaluation of diastolic function, estimation of pulmonary artery pressures. Clinical Applications of Echocardiography Congenital Heart Diseases: Detection and characterization of congenital heart defects, assessment of shunt direction and severity, preoperative planning, and postoperative evaluation. Valvular Heart Diseases: Diagnosis and quantification of valve stenosis and regurgitation, evaluation of valve morphology and function, assessment of prosthetic valve function, guidance for valve repair or replacement. Cardiomyopathies and Heart Failure: Evaluation of left ventricular (LV) and right ventricular (RV) function, detection of wall motion abnormalities, assessment of myocardial viability, monitoring disease progression and response to treatment. Ischemic Heart Disease: Detection of coronary artery disease, assessment of myocardial perfusion and viability, evaluation of wall motion abnormalities and myocardial stunning, guidance for revascularization procedures. Pericardial Diseases: Detection and characterization of pericardial effusion, assessment of pericardial thickness and calcification, evaluation of constrictive pericarditis and cardiac tamponade. Pulmonary Hypertension: Estimation of pulmonary artery pressures, assessment of RV function and size, detection of underlying causes and associated cardiac abnormalities. Infective Endocarditis: Detection of valvular vegetations, assessment of valvular and myocardial involvement, monitoring response to antibiotic therapy, guidance for surgical intervention. Cardiac Masses and Thrombi: Evaluation of intracardiac masses, thrombi, and tumors, differentiation between benign and malignant lesions, assessment of associated hemodynamic effects and embolic risk. Advantages of Echocardiography Non-invasive and Safe: Echocardiography does not involve radiation exposure or the use of contrast agents (unless required for specific indications), making it a safe and preferred imaging modality, especially for pregnant women and patients with renal insufficiency. people searched for : most searches are for: keywords: #besthospitalinnagpur #tophospitalinnagpur #besthospitalnearme #besthospitalinsakkardara #besthospitalinkharbi #besthospitalinumredroad #tophospitalindighori